CAS Number 7647-14-5, Sodium Chloride USP IP BP Ph Eur Analytical Reagent FCC Food Grade Manufacturers Exporters







CAS Number 7647-14-5, Sodium Chloride Manufacturer Exporter
For Properties Specifications of Sodium Chloride Click Properties, Specifications of Sodium Chloride Manufacturer.
For Uses of Sodium Chloride Click Uses of Sodium Chloride Manufacturer.
For For SDS MSDS Sheet of Sodium Chloride Click SDS Safety Data Sheet MSDS Sheet of Sodium Chloride Manufacturer.
The Properties and Specifications of Sodium Chloride:
Sodium Chloride USP Grade Specifications
NaCl -- 58.44
7647-14-5
Sodium Chloride contains not less than 99.0 percent and not more than 100.5 percent of NaCl, calculated on the dried basis.
Appearance of solution: Dissolve 20.0 g of the substance in carbon dioxide-free water, and dilute with the same solvent to 100.0 mL. This solution is clear and colorless.
Identification: It responds to the tests for Sodium and for Chloride.
Chloride: Dissolve about 3 mg of the substance in 2 mL of water. Acidify with diluted nitric acid and add 0.4 mL of silver nitrate TS. Shake, and allow to stand. A curdled, white precipitate is formed. Centrifuge, wash the precipitate with three 1-mL portions of water, and discard the washings. Carry out this operation rapidly in subdued light, disregarding the fact that the supernatant may not become perfectly clear. Suspend the precipitate in 2 mL of water and add 1.5 mL of 10 N ammonium hydroxide. The precipitate dissolves easily with the possible exception of a few large particles, which dissolve more slowly.
Bacterial endotoxins: The level of Bacterial endotoxins are such that the requirement under the relevant dosage form monograph (s) in which the substance is used can be met.
Sterility: Where the label states that the substance is sterile, it meets the requirements for Sterility under the relevant dosage form monograph (s) in which the substance is used.
Acidity or alkalinity: To 20 mL of the solution prepared for the test for Appearance of solution, add 0.1 mL of bromothymol blue TS: not more than 0.5 mL of 0.01 N hydrochloric acid or 0.01 N sodium hydroxide is required to change the color of this solution.
Loss on drying: Dry the test material at 105C for 2 hours: it loses not more than 0.5% of its weight, determined on a 1.000 g sample.
Limit of bromides: To 0.5 mL of the solution prepared for the test for Appearance of solution, add 4.0 mL of water, 2.0 mL of pH 4.7 phenol red TS, and 1.0 mL of chloramine T solution (0.1 mg per mL), and mix immediately. After 2 minutes, add 0.15 mL of 0.1 N sodium thiosulfate, mix, dilute with water to 10.0 mL, and mix. The absorbance of this solution measured at 590 nm, using water as the comparison liquid, is not greater than that of a Standard solution, concomitantly prepared, using 5.0 mL of a solution containing 3.0 mg of potassium bromide per L and proceeding as above, starting with the addition of 2.0 mL of pH 4.7 phenol red TS (0.010%).
Change to read:
Limit of phosphates:
Phosphate stock standard solution— Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of monobasic potassium phosphate in water to obtain a solution having a concentration of about 0.716 mg per mL.
Phosphate standard solution: Dilute 1 mL of the Phosphate stock standard solution with water to 100 mL. Prepare this solution fresh.
Standard solution: Dilute 2 mL of the Phosphate standard solution with water to 100 mL.
Test solution: Dilute 2 mL of the solution prepared in the test for Appearance of solution with water to 100 mL.
Procedure: To the Standard solution and the Test solution, add 4 mL of Sulfomolybdic acid solution, and add 0.1 mL of a mixture of 1 mL of stronger acid stannous chloride TS and 10 mL of 2 N hydrochloric acid. After 10 minutes, compare the colors of 20 mL of each solution: any color in the Test solution is not more intense than that in the Standard solution (0.0025%).
Sulfomolybdic acid solution: Dissolve with heating 2.5 g of ammonium molybdate in 20 mL of water. Dilute 28 mL of sulfuric acid with 50 mL of water, then cool. Mix the two solutions, and dilute with water to 100 mL. USP30
Limit of potassium: (where it is labeled as intended for use in the manufacture of injectable dosage forms, peritoneal dialysis solutions, hem dialysis solutions, or hemofiltration solutions:
Test solution: Transfer 1.00 g of the substance to a 100-mL volumetric flask, add water and swirl to dissolve, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Standard solution: [NOTE—The Standard solution and the Test solution may be modified, if necessary, to obtain solutions of suitable concentrations adaptable to the linear or working range of the instrument.] Dissolve 1.144 g of potassium chloride, previously dried at 105º for 3 hours, in water, dilute with water to 1000 mL, and mix. This solution contains the equivalent of 600 µg of potassium per mL. Dilute as required to obtain not fewer than three solutions at concentrations that span the expected value in the Test solution.
Procedure: Using atomic absorption spectrophotometry, measure, at least three times, the emission intensity of the Test solution and the Standard solution using an air–acetylene flame and a wavelength of 766.5 nm. Prepare a calibration curve from the mean of the readings obtained with the Standard solution, and determine the concentration of potassium in the Test solution. The limit is 0.05%.
Iodides: Moisten 5 g of the substance by the drop wise addition of a freshly prepared mixture of 0.15 mL of sodium nitrite solution (1 in 10), 2 mL of 1 N sulfuric acid, 25 mL of iodide-free starch TS, and 25 mL of water. After 5 minutes, examine the substance in natural light. No blue color is observed.
Aluminum: (where it is labeled as intended for use in the manufacture of peritoneal dialysis solutions, hem dialysis solutions, or hemofiltration solutions)—
Standard aluminum solution: To 352 mg of aluminum potassium sulfate in a 100-mL volumetric flask, add a few mL of water, swirl to dissolve, add 20 mL of diluted sulfuric acid, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Immediately before use, transfer 1.0 mL of this solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
pH 6.0 Acetate buffer: Dissolve 50 g of ammonium acetate in 150 mL of water, adjust with glacial acetic acid to a pH of 6.0, dilute with water to 250 mL, and mix.
Test solution: Dissolve 20.0 g of Sodium Chloride in 100 mL of water, and add 10 mL of pH 6.0
Acetate buffer. Extract this solution with successive portions of 20, 20, and 10 mL of a 0.5% solution of 8-hydroxyquinoline in chloroform, combining the chloroform extracts in a 50-mL volumetric flask. Dilute the combined extracts with chloroform to volume, and mix.
Standard solution: Prepare a mixture of 2.0 mL of Standard aluminum solution, 10 mL of pH 6.0 Acetate buffer, and 98 mL of water. Extract this mixture as described for the Test solution, dilute the combined extracts with chloroform to volume, and mix.
Blank solution: Prepare a mixture of 10 mL of pH 6.0 Acetate buffer and 100 mL of water. Extract this mixture as described for the Test solution, dilute the combined extracts with chloroform to volume, and mix.
Procedure: Determine the fluorescence intensities of the Test solution and the Standard solution in a fluorometer set at an excitation wavelength of 392 nm and an emission wavelength of 518 nm, using the Blank solution to set the instrument to zero.
The fluorescence of the Test solution does not exceed that of the Standard solution (0.2 µg per g).
Magnesium and alkaline-earth metals: To 200 mL of water add 0.1 g of hydroxylamine hydrochloride, 10 mL of pH 10.0 ammonia–ammonium chloride buffer (prepared by dissolving 5.4 g of ammonium chloride in 20 mL of water, adding 20 mL of ammonium hydroxide and diluting to 100 mL), 1 mL of 0.1 M zinc sulfate, and about 0.2 g of eriochrome black T trituration. Heat to about 40º. Titrate this solution with 0.01 M edetate disodium VS until the violet color changes to deep blue. To this solution add 10.0 g of Sodium Chloride dissolved in 100 mL of water. If the color changes to violet, titrate the solution with 0.01 M edetate disodium VS to a deep blue endpoint.
The volume of 0.01 M edetate disodium consumed in the second titration does not exceed 2.5 mL
(0.01%, calculated as Ca).
Arsenic: 1 µg per g.
Iron:
Test solution: Use a 10-mL portion of the solution prepared for the test for Appearance of solution.
Standard solution: Immediately before use, dilute Standard Iron Solution (see Iron 241 ) 1 to 10 with water. This solution contains the equivalent of 1 ?g of iron per mL. Combine 4 mL of this solution and 6 mL of water.
Procedure: To each of the solutions, add 2 mL of a 200 g per L solution of citric acid and 0.1 mL of thioglycolic acid. Mix, make alkaline with stronger ammonia water, and dilute with water to 20 mL. After 5 minutes, any pink color in the Test solution is not more intense than that from the Standard solution.
The limit is 2 µg per g.
Barium: To 5 mL of the solution prepared for the test for Appearance of solution, add 2 mL of 2 N sulfuric acid and 5 mL of water. To another 5 mL of the solution prepared for the test for Appearance of solution, add 7 mL of water. The solutions are equally clear after standing for 2 hours.
Ferrocyanides: Dissolve 2.0 g in 6 mL of water. Add 0.5 mL of a mixture of 5 mL of ferric ammonium sulfate solution (1 g in 100 mL of 0.1 N sulfuric acid) and 95 mL of ferrous sulfate solution (1 in 100): no blue color develops in 10 minutes.
Sulfate:
Standard sulfate solution A: To 181 mg of potassium sulfate in a 100-mL volumetric flask, add a few mL of 30% alcohol, swirl to dissolve, dilute with 30% alcohol to volume, and mix. Immediately before use, transfer 10.0 mL of this solution to a 1000-mL volumetric flask, dilute with 30% alcohol to volume, and mix. This solution contains 10 µg of sulfate per mL.
Standard sulfate solution B: To 181 mg of potassium sulfate in a 100-mL volumetric flask, add a few mL of water, swirl to dissolve, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Immediately before use, transfer 10.0 mL of this solution to a 1000-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix. This solution contains 10 micgm of sulfate per mL.
Sodium chloride solution: Dissolve 2.5 g of Sodium Chloride in 50 mL of water.
Procedure: To 1.5 mL of Standard sulfate solution A add 1 mL of a barium chloride solution (1 in 4), shake, and allow to stand for 1 minute. To 2.5 mL of the resulting suspension, add 15 mL of the Sodium chloride solution and 0.5 mL of 5 N acetic acid, and mix (Test solution). Prepare the Standard solution in the same manner, except use 15 mL of Standard sulfate solution B instead of the Sodium chloride solution: any turbidity produced in the Test solution after 5 minutes standing is not greater than that produced in the Standard solution (0.020%).
Nitrites: To 10 mL of the solution prepared in the test for Appearance of solution, add 10 mL of water, and measure the absorbance of the solution in a 1-cm cell at 354 nm. The absorbance is not greater than 0.01.
Heavy metals: 5 ppm.
Sodium Chloride BP Ph Eur Grade Specifications
NaCl -- 58.44 -- CAS 7647-14-5
Action and use: Used in treatment of electrolyte deficiency.
DEFINITION
Content: 99.0 per cent to 100.5 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals or white or almost white pearls.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water, practically insoluble in anhydrous ethanol.
IDENTIFICATION
A. It gives the reactions of chlorides.
B. It gives the reactions of sodium.
TESTS
Solution S: If the substance is in the form of pearls crush before use.
Dissolve 20.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water prepared from distilled water and dilute to 100.0 ml with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution: Solution S is clear and colourless.
Acidity or alkalinity: To 20 ml of solution S add 0.1 ml of bromothymol blue solution. Not more than 0.5 ml of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid or 0.01 M sodium hydroxide is required to change the colour of the indicator.
Bromides: Maximum 100 ppm.
Ferrocyanides: Dissolve 2.0 g in 6 ml of water. Add 0.5 ml of a mixture of 5 ml of a 10 g/l solution of ferric ammonium sulphate in a 2.5 g/l solution of sulphuric acid and 95 ml of a 10 g/l solution of ferrous sulphate. No blue colour develops within 10 min.
Iodides: Moisten 5 g by the drop wise addition of a freshly prepared mixture of 0.15 ml of sodium nitrite solution, 2 ml of 0.5 M sulphuric acid , 25 ml of iodide-free starch solution and 25 ml of water. After 5 min, examine in daylight. The mixture shows no blue colour.
Nitrites: To 10 ml of solution S add 10 ml of water. The absorbance is not greater than 0.01 at 354 nm.
Phosphates: Maximum 25 ppm.
Sulphate: Maximum 200 ppm.
Aluminium: Maximum 0.2 ppm, if intended for use in the manufacture of peritoneal dialysis solutions, hem dialysis solutions or haemofiltration solutions.
Arsenic: Maximum 1 ppm, determined on 5 ml of solution S.
Barium: To 5 ml of solution S add 5 ml of distilled water and 2 ml of dilute sulphuric acid. After 2 h, any opalescence in the solution is not more intense than that in a mixture of 5 ml of solution S and 7 ml of distilled water.
Iron: Maximum 2 ppm, determined on solution S.
Magnesium and alkaline-earth metals: Maximum 100 ppm, calculated as Ca and determined on 10.0 g.
Potassium: maximum 5.00 × 102 ppm, if intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral dosage forms or hem-dialysis, haemofiltration or peritoneal dialysis solutions.
Atomic emission spectrometry: To pass the test
Heavy metals: Maximum 5 ppm.
Loss on drying: Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105C for 2h.
Bacterial endotoxins: Less than 5 IU/g, if intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral dosage forms without a further appropriate procedure for removal of bacterial endotoxins.
Specifications of NaCl, Sodium Chloride IP Grade Specifications:
Dry Basis Assay: 99.0% - 100.5%
Description: White, crystalline powder.
Solubility: Freely soluble in water; practically insoluble in ethanol.
Acidity or alkalinity: Passes Test
Clarity and Colour of Solution: Clear & colourless solution (10% w/w).
Arsenic: 1 ppm maximum.
Barium: Passes Test
Bromide: 0.1% maximum.
Calcium & Magnesium as Ca: 50 ppm maximum.
Ferro cyanide: Passes Test
Heavy Metals: 5 ppm maximum.
Iodide: Passes Test
Iron: 20 ppm maximum.
Loss on Drying: 1% maximum.
Potassium: 0.1% maximum.
The Uses of Sodium Chloride:
Sodium chloride is used as an electrolyte replenisher to help prevent heat cramps caused by too much sweating. This medicine is also used for the preparation of normal isotonic solution of sodium chloride. Sodium chloride is used in medical treatments such as IV infusions and catheter flushes. Sodium chloride is used to treat or prevent sodium loss caused by dehydration, excessive sweating, or other causes. It is widely used in food industries as a food preservative and as a flavour enhancer.
The MSDS-SDS Hazard Statement of Sodium Chloride:
Sodium Chloride SDS, Safety Data Sheet
MSDS Sheet, Material Safety Data Sheet 24-Jul-23
Section 1 - Chemical Product and Identification
Product Name & Other Names: Sodium Chloride or Common salt or Halite or Rock salt or Saline or Salt or Sea salt or Table salt.
CAS Number: 7647-14-5
EINECS EC Code: 231-598-3
Chemical Formula: NaCl
Molecular Weight: 58.44
Relevant uses and uses advised against (if any): Laboratory Chemicals and Industrial Manufacturing Use.
Section 2 - Hazards Identification
GHS, Globally Harmonized System Classification in accordance with 29 CFR 1910
Classification according to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008
Not a hazardous substance or mixture according to Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008.
This substance is not classified as dangerous according to Directive 67/548/EEC.
Labeling according TO GHS & Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008
GHS Label Elements NONE |
Signal Word: None
Precautionary statements:
P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
P262: Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing.
P281: Use personal protective equipment as required.
P302+P352 - IF ON SKIN: Wash with plenty of soap and water.
P304 + P340 - IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing.
P305 + P351 + P338 - IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing.
Section 3 - Composition, Information on Ingredients
Product Name & Other Names: Sodium Chloride or Common salt or Halite or Rock salt or Saline or Salt or Sea salt or Table salt.
CAS#: 7647-14-5
EINECS EC No.: 231-598-3
Section 4 - First Aid Measures
Always seek medical advice after the first aid treatment.
Eyes: Flush eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes, occasionally lifting the upper and lower eyelids. Get medical aid.
Skin: Flush skin with plenty of soap and water for at least 15 minutes while removing contaminated clothing and shoes. Get medical aid if irritation develops or persists. Wash clothing before reuse.
Ingestion: If victim is conscious and alert, give 2-4 cupfuls of milk or water. Get medical aid. Wash mouth out with water.
Inhalation: Remove from exposure to fresh air immediately. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. Get medical aid if cough or other symptoms appear.
Section 5 - Fire Fighting Measures
General Information: Water runoff can cause environmental damage. Dike and collect water used to fight fire. Wear appropriate protective clothing to prevent contact with skin and eyes. Wear a self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) to prevent contact with thermal decomposition products. Substance is noncombustible.
Extinguishing Media: For small fires, use water spray, dry chemical, carbon dioxide or chemical foam.
Special hazards arising from the substance: Hydrogen chloride gas, Sodium oxides.
Special Information: In the event of a fire, wear full protective clothing and NIOSH-approved self-contained breathing apparatus with full face piece operated in the pressure demand or other positive pressure mode. At high temperatures under fire conditions, it may produce toxic or irritating fumes. Fire-extinguishing work is done from the windward and the suitable fire-extinguishing method according to the surrounding situation is used.
Section 6 - Accidental Release Measures
Personal precautions, protective equipment, and emergency procedures: Avoid breathing dust/fumes/gas/mist/vapors/spray. Use individual protective equipment (waterproof boots, suitable protective clothing, safety glasses, etc.). Do not approach facing the wind.
Environmental precautions: Do not let the product enter drains, soil, or water sources.
Methods and materials used for containment Cleanup procedures and Storage: Do not inhale vapors, mist, or gas. Avoid dust formation. Contain spilled material. Cover with an inert, non-combustible absorbent material, (e.g. sand, earth, diatomaceous earth, vermiculite). Use a shovel to put the material into a convenient waste disposal container.
Section 7 - Handling and Storage
Precautions for safe handling: Apply according to good manufacturing and industrial hygiene practices. Ensure proper ventilation. In case of insufficient ventilation, wear suitable respiratory equipment. Wash thoroughly after handling. Do not drink, eat, or smoke while handling. Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and clothing. Minimize dust generation. Avoid breathing dust/fumes/gas/mist/vapors/spray. Keep container tightly closed. Avoid ingestion and inhalation. Use individual protective equipment (waterproof boots, suitable protective clothing, safety glasses, etc.).
Conditions for safe storage, including any incompatibilities: Store in cool, dry, and ventilated area away from heat sources and protected from sunlight in tightly closed original container. Keep air contact to a minimum. Store protected from heat, sparks and ignition sources and incompatible materials. Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid inhalation of dust/mist/vapor. Do not store with incompatible materials like strong oxidizing agents, iron, or steel, building materials (such as cement), bromine, or trifluoride. Store protected from moisture.
Section 8 - Exposure Controls, Personal Protection
Engineering Controls: Good general ventilation should be sufficient to control airborne levels. Facilities storing or utilizing the material should be equipped with an eyewash facility and a safety shower.
Ventilation System: A system of local and/or general exhaust is recommended to keep employee exposures as low as possible.
Personal Respirators (NIOSH Approved): For conditions of use where exposure to dust or mist is apparent and engineering controls are not feasible, a particulate respirator may be worn.
Skin Protection: Wear protective gloves and clean body-covering clothing.
Eye Protection: Use chemical safety goggles and/or full face shield where dusting or splashing of solutions is possible. Maintain eye wash fountain and quick-drench facilities in work area.
Other Control Measures: Maintain good housekeeping in work area. Handle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice.
Section 9 - Physical and Chemical Properties
Appearance: Solid. Colorless or white crystalline powder.
Odor: Odorless
Odor threshold: Not available.
pH: Not available.
Relative density: around 2.16
Boiling Point: 2575 deg F
Freezing/Melting Point:1474 deg F
Flash point: Not available.
Auto-ignition temperature: Not available.
Decomposition temperature: Not available.
Upper/lower flammability or explosive limits: Not available.
Vapor pressure: Not available.
Vapor density: Not available.
Evaporation rate: Not available.
Flammability (solid, gas): Not available.
Partition coefficient: n-octanol/water: Not available.
Solubility: Soluble in water.
Viscosity: Not available.
Section 10 - Stability and Reactivity
Chemical Stability: Stable.
Conditions to Avoid: High temperatures, exposure to moist air or water.
Incompatibilities with Other Materials: It reacts with most non-noble metals such as iron or steel, building materials (such as cement), bromine, or trifluoride. Potentially explosive reaction with dichloro-maleic anhydride + urea. Electrolysis of mixtures with nitrogen compounds may form explosive nitrogen tri-chloride.
Hazardous Decomposition Products: Toxic fumes of chlorine or hydrogen chloride and sodium oxide.
Hazardous Polymerization: Has not been reported.
Section 11 - Toxicological Information
LD50 Oral - Rat - 3,550 mg/kg (Sodium chloride)
LC50 Inhalation - Rat - 1 h - > 42,000 mg/m3 (Sodium chloride)
LD50 Dermal - Rabbit - > 10,000 mg/kg( Sodium chloride)
Carcinogenicity: No component of this product present at levels greater than or equal to 0.1% is identified as possible or confirmed human carcinogen by IARC, ACGIH, OSHA and NTP.
Mutagenic Effects: Not available.
Developmental Toxicity: Not available.
Reproductive Effects: No information available.
Section 12 - Ecological Information
Toxicity to fish: LC50 - Lepomis macrochirus (Bluegill) - 5,840 mg/l - 96 h
Toxicity to daphnia and other aquatic invertebrates:
NOEC - Daphnia (water flea) - 1,500 mg/l - 7 d(Sodium chloride)
LC50 - Daphnia magna (Water flea) - 1,661 mg/l - 48 h(Sodium chloride)
Results of PBT and vPvB assessment: This substance/mixture contains no components considered to be either persistent, bioaccumulative and toxic (PBT), or very persistent and very bioaccumulative (vPvB) at levels of 0.1% or higher.
Section 13 - Disposal Considerations
Chemical waste generators must determine whether a discarded chemical is classified as a hazardous waste. US EPA guidelines for the classification determination are listed in 40 CFR Parts 261.3.
Section 14 - Transport Information
DOT USA, TDG Canada & ADR/RID Europe: Not controlled.
IMDG/IMO: Not controlled.
IATA/ICAO: Not controlled.
Section 15 - Regulatory Information
USA Regulations:
SARA 311/312 Hazards: See section 2.
California Prop. 65 Components: This product does not contain any chemicals known to State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, or any other reproductive harm.
DISCLAIMER: The information and recommendations set forth herein are presented in good faith and believed correct as of the date hereof. It is compiled from various sources and it is not necessarily all inclusive nor fully adequate in every circumstance. In addition, these suggestions should not be confused with nor followed in violation of applicable laws, regulations, rules or insurance requirements applicable. This MSDS sheet is intended only as a guide to the appropriate precautionary handling of the material by a properly trained person using this product. Individuals receiving the information must exercise their independent judgment in determining its appropriateness for a particular purpose.
Anmol Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd. is an off-shoot of Anmol Chemicals Taloja. It is located in MIDC Taloja and it is manufacturing pharmaceutical grades of API, Excepients, Food grade and Reagent grade chemicals. Anmol Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd. is a several decades old group of companies, engaged in manufacturing, supplying, distributing, wholesale supplies for actual users, retail or small pack supplies for research and development chemicals, fine and speciality chemicals, pharmaceutical excipients, mineral fortifiers in chemically pure, Analytical reagent grade, IP BP USP Ph Eur EP JP and other pharmaceutical grade monograph including FCC Food grade chemicals and Nutraceuticals, Mineral Fortifiers at best prices.
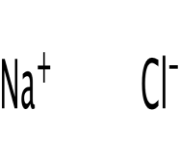
Sodium Chloride Structure
CAS Number 7647-14-5, Sodium Chloride Manufacturer Exporter
ANMOL CHEMICALS & PHARMACEUTICALS Pvt. Ltd.
India, USA, Europe, UAE
TELEPHONE: +912223770100
Navi Mumbai, INDIA
e-mail: info(At the rate i.e. @)anmol.org
Copyright. 24-nov-24
We manufacture:
Glacial Acetic Acid Manufacturer
Aluminum Chloride Hexahydrate Anhydrous
Aluminum Chlorohydrate Solution Powder
Copper Chloride, Cupric Chloride, Cuprous Chloride
Ferric Chloride Anhydrous Hexahydrate

